Economies of scale are cost advantages of a company due to its large size. Most companies and businesses can realize advantages of scale that are a result of two effects:
Fixed costs - spread across a large volume of units, decreasing the cost per unit
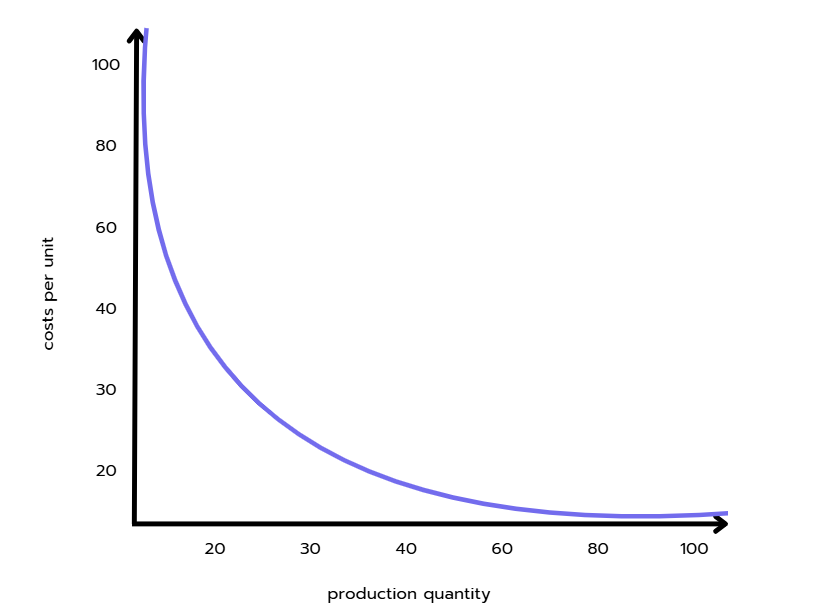
- Variable costs - low due to operational efficiencies and synergies
- Larger production processes can be split into smaller, repetitive, and simpler tasks.
- Larger sizes of raw materials and production technologies, resulting in bulk discounts.
- Risks are distributed on a larger scale, leading to fewer demand peaks.
- Cheap automatized production technologies become feasible.
Example:
A power supplier has high initial costs for setting up the infrastructure. Once the infrastructure is set up, the additional costs of providing their service to an additional household are very little. Fixed costs will be split into more households and sudden demand drops have less impact because other households still require sufficient energy levels.
Want to see a full case of how to apply the concept of Economies of Scale? Solve the Paper Print case: