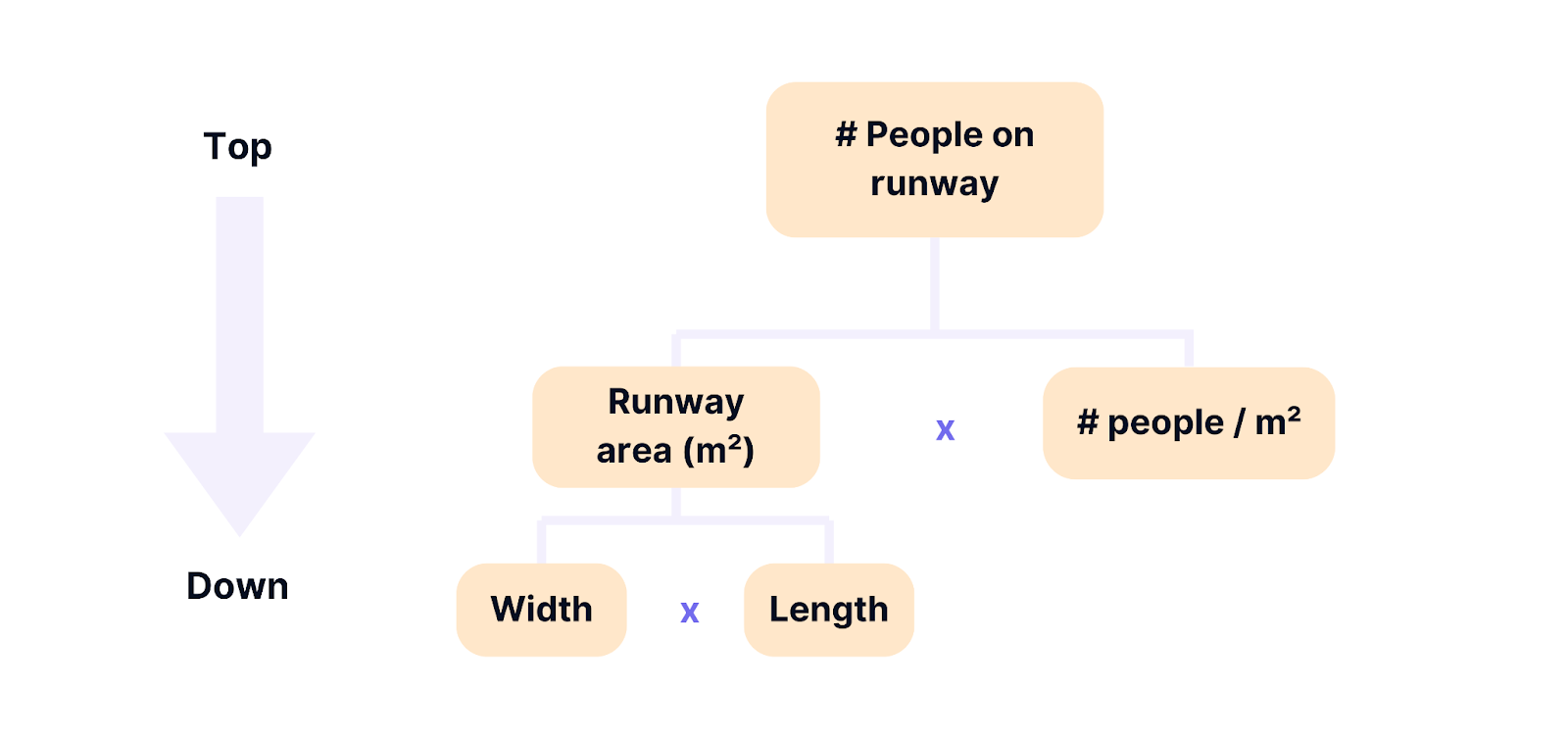
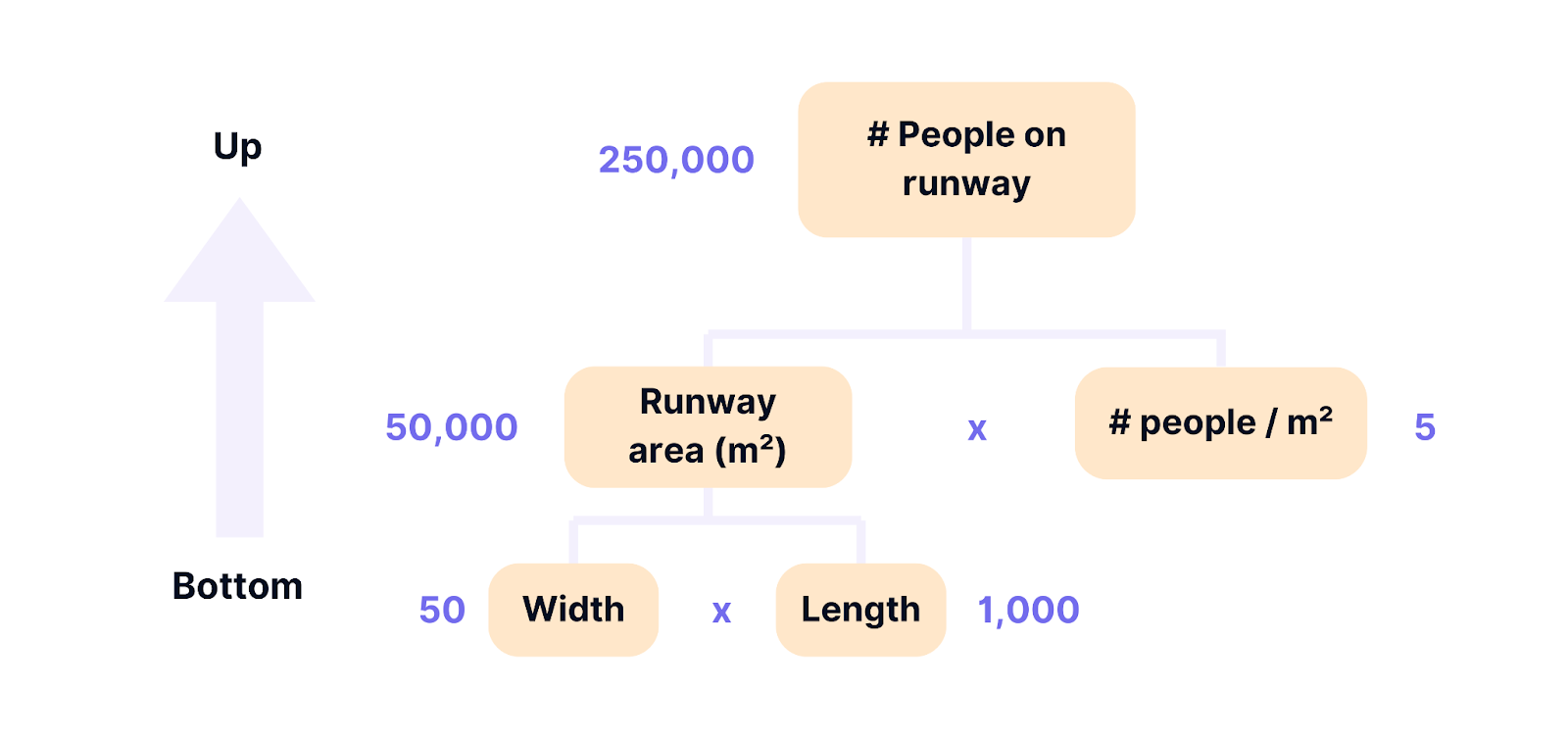
The Issue Tree is a valuable tool for analyzing the causes of issues during a case interview. When faced with a complex issue, the Issue Tree helps you break it down into its components. By focusing on the most urgent aspects and employing a hypothesis-driven approach, you can progress more quickly—a skill highly valued in consulting. 🚀
🔎 In this article, you'll learn how to effectively use the Issue Tree, understand the differences between problem-based and solution-based trees, and how to leverage this technique to excel in your case interviews.
Problem-Based Tree vs. Solution-Based Tree
In case interviews, two main types of Issue Trees are utilized:
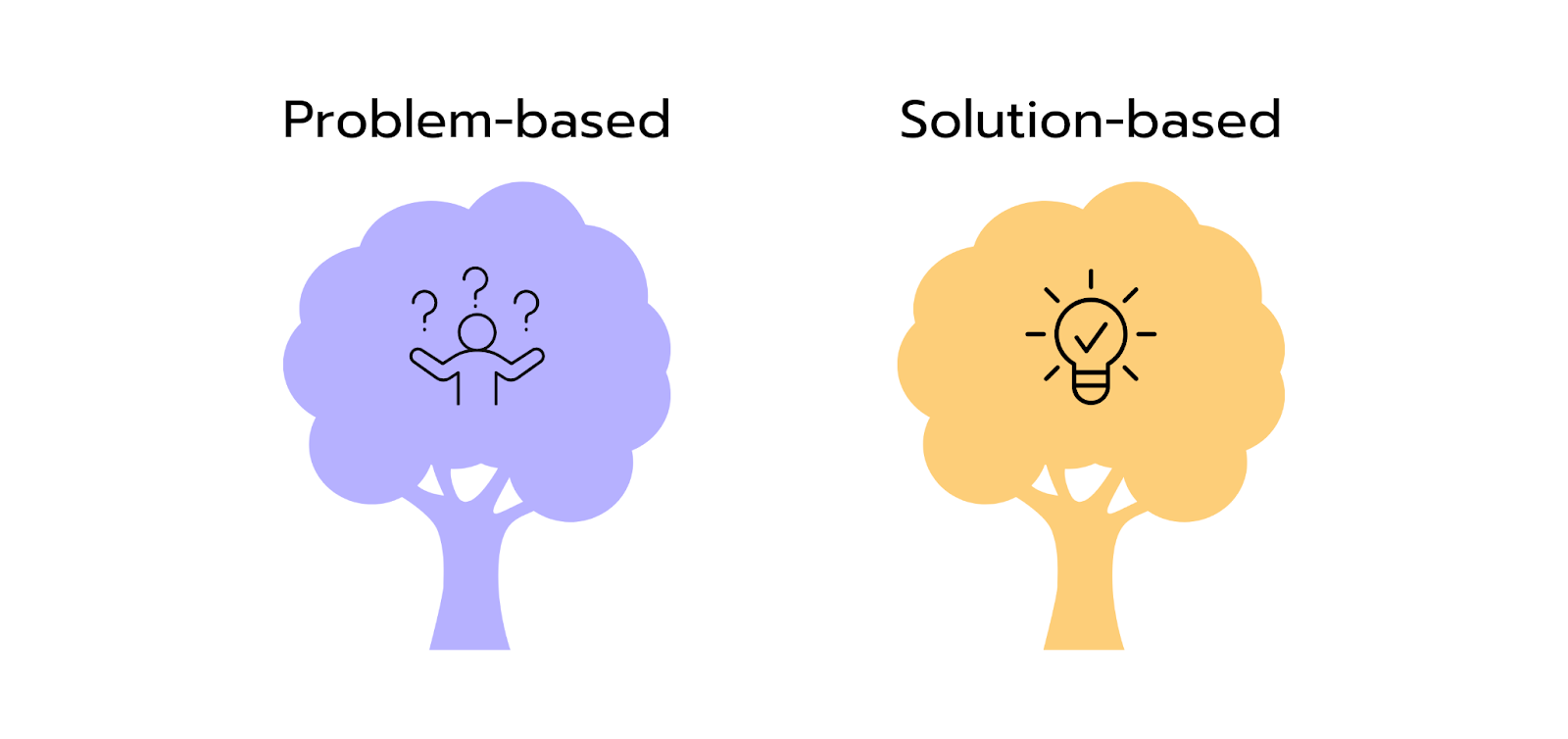
- Problem-Based Tree: This helps you identify and understand the root causes of the issue and why it occurred in the first place.
- Solution-Based Tree: This is used to develop recommendations and clarify how the issue can be resolved.
Ensure that the issues are MECE (mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive). Otherwise, it will be challenging to address each area effectively. Use a hypothesis-driven approach to tackle the most significant issues first (see Pareto Principle).
In consulting, the preferred approach is "answer-first" or "results-first." This involves starting with the main solution or conclusion and then working out the rationale. This is closely related to the Pyramid Principle.
💡 Prep Tip: Practice these and other essential frameworks with our drills!