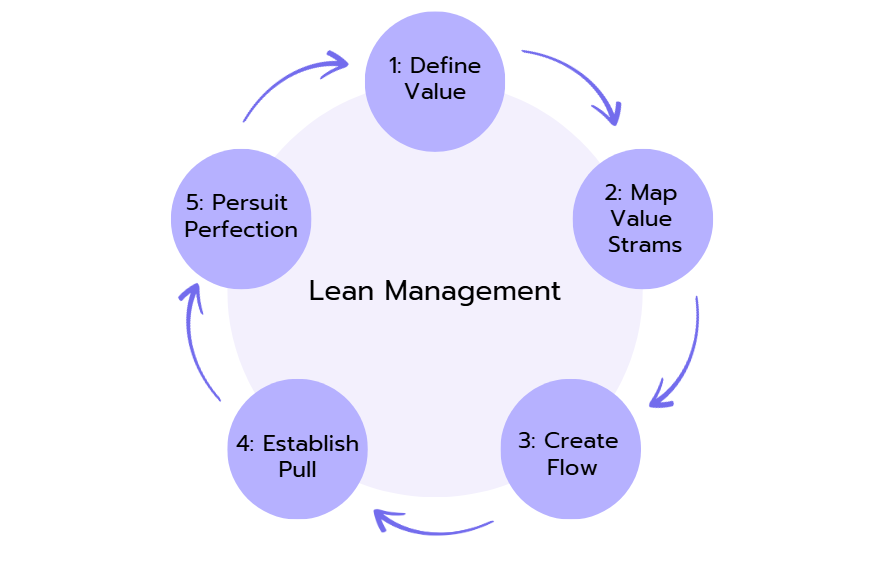
Lean Management is a business methodology derived from the Toyota Production System (TPS) that focuses on reducing waste (non-value-adding activities) in order to improve customer value. The methodology relies on continuous improvement (Kaizen) and respect for people as foundational principles, promoting efficiency, responsiveness, and quality through the elimination of waste in processes, products, and services. Furthermore, it is an agile methodology like the Scrum Framework or Kanban (which also relies on Kaizen and has a Toyota connection).
Important Things to Know About Lean Management
When delving into Lean Management, it's crucial to consider both its benefits and challenges. Here's a brief overview of the key pros and cons associated with this approach:
Pros:
- Efficiency improvement: By focusing on eliminating waste, Lean Management can lead to increased efficiency, allowing organizations to do more with less.
- Cost reduction: Less waste means lower costs, which can improve profitability.
- Increased customer satisfaction: The goal of Lean Management is to provide more value to the customer, which can lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction.
- Improved quality: Lean emphasizes identifying and resolving issues at their source, which can lead to improvements in product or service quality.
- Empowers employees: Lean Management values employee input and encourages workers to identify and solve problems, promoting a sense of ownership and engagement.
Cons:
- Implementation challenges: Adopting Lean Management requires a significant shift in organizational culture, which can be difficult and time-consuming to achieve.
- Short-term focus: Some critics argue that the focus on efficiency and waste reduction can lead to short-term thinking, potentially at the expense of long-term strategic goals.
- Risk of over-standardization: While standardization is a key element of lean management, if not well managed, it can lead to a lack of creativity and innovation.
- Employee stress: The continuous pressure to improve and eliminate waste can lead to increased stress and burnout among employees.
- Possible quality issues: If not properly implemented or monitored, Lean Management practices could potentially lead to quality issues as resources are reduced.
Conclusion
Understanding Lean Management is essential for consultants across industries. As a powerful methodology focused on eliminating waste and maximizing customer value, it's an effective tool in a consultant's arsenal for driving organizational transformation. Recognizing the principles of Lean, consultants can offer strategic insights to organizations, aiding them in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing customer satisfaction.
However, it's equally important to comprehend the challenges associated with Lean implementation. A shift towards a lean culture requires comprehensive organizational change and a thoughtful balancing of efficiency and innovation. As such, a consultant's knowledge of Lean Management goes beyond just understanding the concept. It's about mastering the art of implementation, mitigating potential pitfalls, and adapting Lean principles to the unique needs of every organization. This ability will ultimately differentiate a good consultant from a great one.
Hence, in an era where organizations are under constant pressure to deliver more with less, Lean Management emerges as a crucial concept that every consultant must be well acquainted with.