Correlation and causality are two important terms in statistics that are often confused with each other. In this text, the difference between the two is explained with understandable examples and related to the business consulting industry. Keep in mind that math is an important aspect of the case interview.
The Principle of Correlation
Correlation describes the degree of relationship between two variables. When two variables correlate, it means that changes in one variable are accompanied by changes in the other variable. A positive correlation occurs when the values of both variables increase or decrease together. An example of a positive correlation is the relationship between the number of hours spent preparing for an exam and the score achieved. As a rule, the more time one invests, the better the exam score.
A negative correlation occurs when the values behave in opposite ways, that is, when the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases, and vice versa. As an example, there may be a negative correlation between the number of hours one spends watching TV and physical fitness. The more time one spends in front of the TV, the less time one has for physical activities, which can lead to lower fitness.
However, it is important to understand that correlation alone is not sufficient to conclude causality.
The Principle of Causality
Causality means that a change in one variable is a direct cause of a change in another variable. In other words, one variable causes a change in another variable. An example often used to explain the difference between correlation and causality is the relationship between the number of ice cream sales and the number of sunburns. There is a positive correlation between these two variables because more ice cream is sold on sunny days and more people also get sunburned. However, it would be wrong to assume that ice cream consumption causes sunburns. In reality, the common cause of both is sun exposure. On sunny days, people buy more ice cream and are also at higher risk of sunburn. This example illustrates that correlation does not automatically indicate causation.
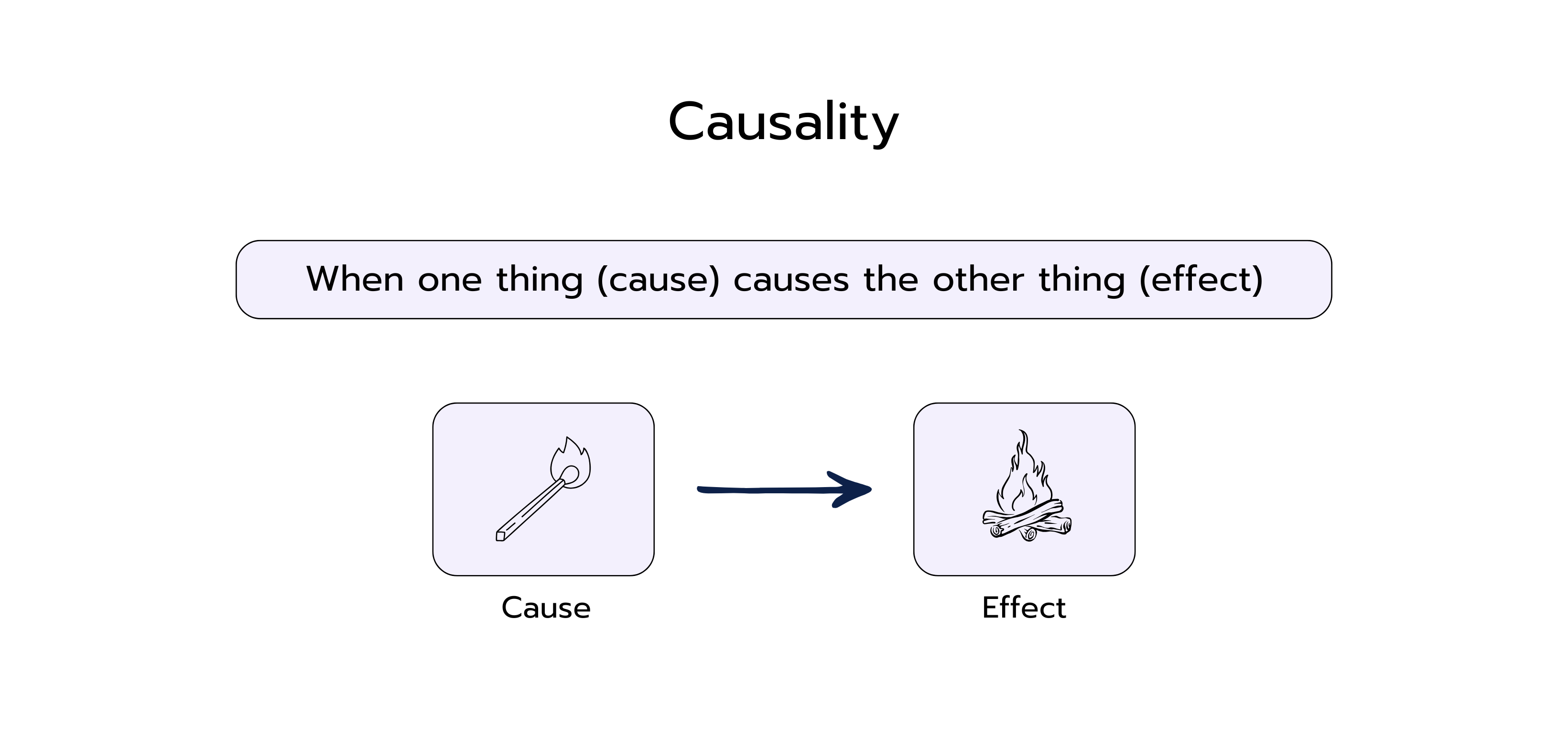
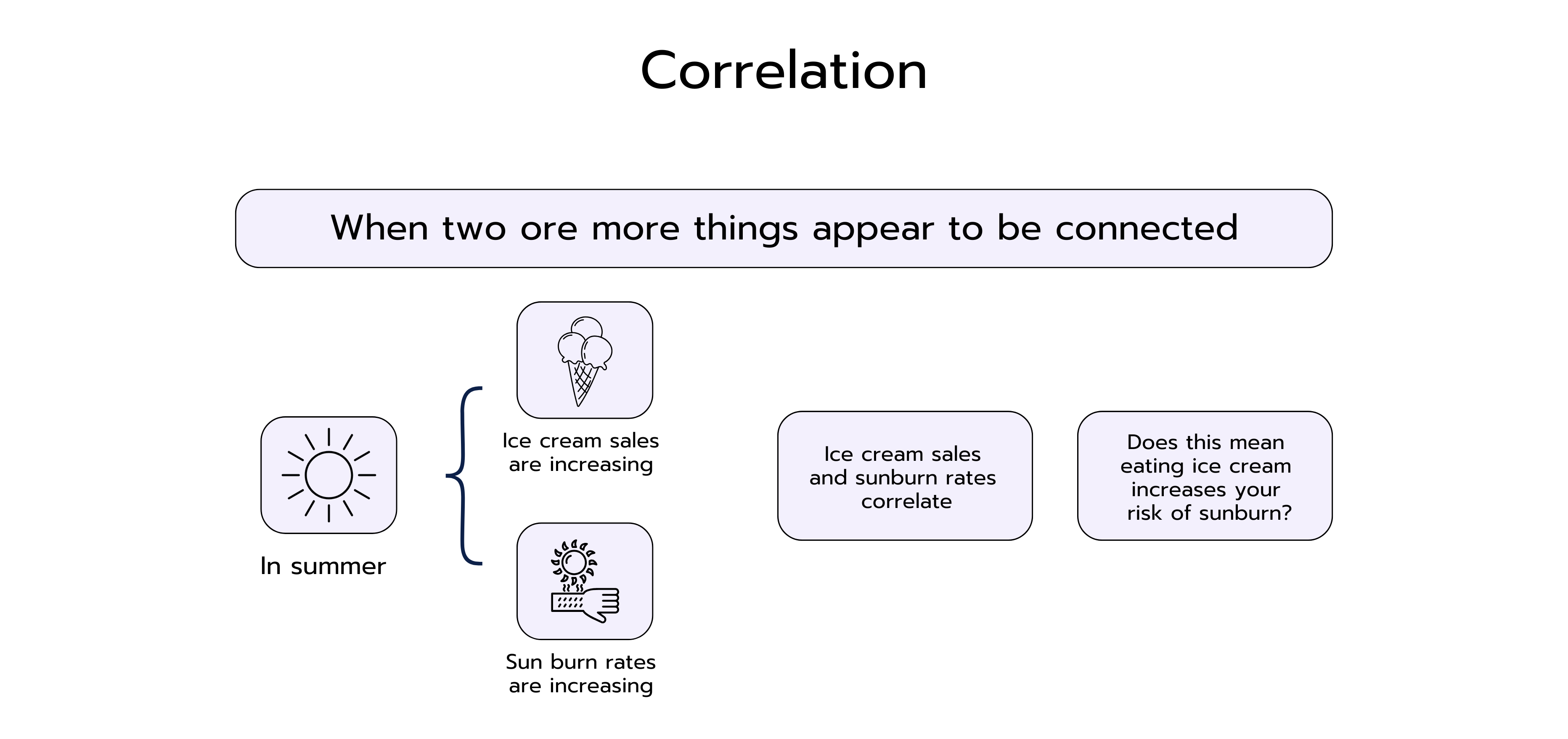
=> Correlation does not always mean causalty!
Correlation and Causality in Management Consulting
In consulting, understanding correlation and causality can play a critical role. When consultants analyze data to help companies or organizations, it is important that they draw the right conclusions and not make false assumptions. Usually it is important to decide which factors should be qualitative and/or quantitative analyzed.
Let's say a company finds that there is a strong correlation between the use of a particular marketing strategy and sales growth. The company might be tempted to assume that the marketing strategy is directly responsible for sales growth and therefore continue to invest heavily in that strategy. However, it could be that the correlation only indicates that both variables are influenced by another, as yet unknown, cause. To confirm causality, further research would be required, such as experiments or bigger control groups to test the direct impact of marketing strategy on sales. Possible causes could also be pricing, a change in the product portfolio or the changing size of the market.
Overall, it is important to understand that correlation and causality are different concepts. Correlation simply describes the relationship between two variables, while causality implies a cause-and-effect relationship. Just because two variables correlate does not automatically mean that one variable is the cause of the change in the other variable. Further investigation and evidence is needed to conclude causality.