Interessierst du dich für den Finanzbereich und möchtest dazu beitragen, dass große Ideen Realität werden? Dann könnte Venture Capital genau dein Ding sein! Hier dreht sich alles darum, junge und innovative Start-ups zu fördern – Unternehmen mit bahnbrechenden Ideen und beeindruckendem Potenzial. Werfen wir gemeinsam einen Blick auf diese spannende Branche. Auf geht’s!
Dein Weg ins Venture Capital
Was ist Venture Capital?
Beim Venture Capital (VC), auch Risikokapital genannt, wird Kapital in junge, wachstumsstarke Unternehmen investiert, die sich häufig noch in einer frühen Entwicklungsphase befinden. Diese Start-ups verfügen oft über innovative Geschäftsideen oder Technologien, haben jedoch noch keinen etablierten Marktzugang oder nachhaltige Gewinne erzielt.
Venture-Capital-Fonds spielen dabei eine zentrale Rolle. Diese Fonds bündeln Kapital von Investor:innen wie institutionellen Anlegern, vermögenden Privatpersonen oder Pensionskassen und investieren gezielt in vielversprechende Start-ups. Oft sind die Fonds auf bestimmte Branchen spezialisiert – etwa Technologie, Biotechnologie oder Nachhaltigkeit – und können dadurch gezielt Marktchancen identifizieren und nutzen.
Die Investitionen dienen dazu, den Start-ups die finanziellen Mittel bereitzustellen, die sie benötigen, um ihre Produkte oder Dienstleistungen weiterzuentwickeln, zu skalieren und erfolgreich am Markt zu etablieren. Das ist wichtig – so werden Innovationen vorangetrieben, Arbeitsplätze geschaffen und ganze Branchen verändert.
Im Gegensatz zu Private Equity, das meist in etablierte Unternehmen investiert, ist Venture Capital mit einem höheren Risiko verbunden, da die Erfolgschancen von Start-ups unsicher sind.
👉 Du willst mehr über die Unterschiede zwischen VC und PE erfahren? Dann lies unseren Artikel!
So funktioniert der Auswahl- und Investmentprozess im Venture Capital
Der Weg von der Idee bis zur Investition in ein Start-up ist im Venture Capital durch einen klar strukturierten Prozess geprägt. Dabei spielen die Auswahl der richtigen Unternehmen und der Zeitpunkt der Investition eine zentrale Rolle.
Wie ist der typische Ablauf einer Venture-Capital-Investition?
Der Investmentprozess im Venture Capital ist darauf ausgelegt, die besten Start-ups mit hohem Potenzial zu finden und gezielt zu fördern. Der Ablauf folgt dabei einem klaren Schema, das aus mehreren Schritten besteht:
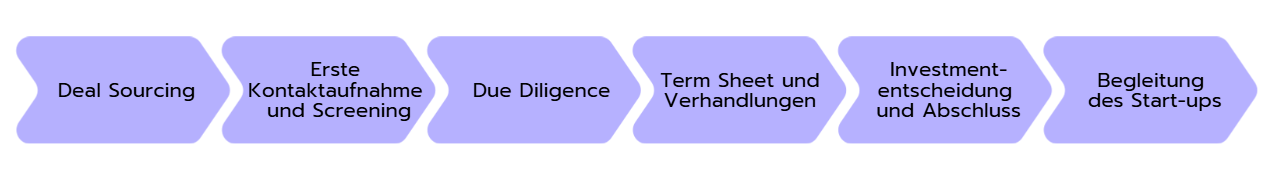
- Deal Sourcing:
Alles beginnt mit der Suche nach spannenden Start-ups. Venture-Capital-Unternehmen nutzen hierfür verschiedene Kanäle wie Netzwerke, Pitch-Events, Gründer-Plattformen oder direkte Bewerbungen von Start-ups. Ziel ist es, möglichst früh auf vielversprechende Ideen aufmerksam zu werden, bevor sie von anderen Investor:innen entdeckt werden.
- Erste Kontaktaufnahme und Screening:
Sobald ein interessantes Start-up identifiziert wurde, erfolgt eine erste Kontaktaufnahme und Einschätzung. Das Team prüft, ob das Geschäftsmodell, die Idee und der Markt grundsätzlich zur Investmentstrategie passen. Hier geht es vor allem um den „ersten Eindruck“ – sowohl von der Idee als auch vom Gründerteam.
- Due Diligence:
Stimmt die Grundvoraussetzung, startet eine ausführliche Prüfung. In dieser Phase wird analysiert, wie tragfähig das Geschäftsmodell ist, wie groß das Marktpotenzial scheint und wie kompetent das Gründerteam aufgestellt ist. Außerdem werden rechtliche, finanzielle und technologische Aspekte geprüft.
- Term Sheet und Verhandlungen:
Nach einer positiven Due Diligence wird ein Term Sheet aufgesetzt, in dem die grundlegenden Investitionsbedingungen festgelegt werden. Hier geht es unter anderem um die Höhe der Investition, den Unternehmensanteil für die Investor:innen und mögliche Mitspracherechte. Dieser Schritt erfordert häufig intensive Verhandlungen zwischen beiden Seiten.
- Investmententscheidung und Abschluss:
Ist das Term Sheet finalisiert, wird die Investitionsentscheidung offiziell getroffen. Die Vertragsunterzeichnung markiert den Abschluss dieser Phase. Das Kapital wird bereitgestellt, und die Zusammenarbeit beginnt.
- Begleitung des Start-ups:
Nach der Investition unterstützen Venture-Capital-Unternehmen die Start-ups aktiv. Sie bringen ihre Expertise ein, helfen bei strategischen Entscheidungen und öffnen Netzwerke, um das Wachstum zu beschleunigen. Diese Unterstützung kann entscheidend sein, um die gesteckten Ziele zu erreichen.
Welche Start-ups sind interessant für Venture-Capital-Unternehmen?
Mehrere Faktoren entscheiden über die Wahl geeigneter Unternehmen:
- Innovative Geschäftsideen: Lösungen, die Probleme effektiv angehen, neue Märkte schaffen oder bestehende Strukturen disruptiv verändern, bieten großes Potenzial für hohe Renditen.
- Hohes Wachstumspotenzial: Start-ups mit großem Marktvolumen, steigender Nachfrage und schneller Skalierbarkeit sind besonders attraktiv und versprechen langfristige Rentabilität.
- Skalierbare Geschäftsmodelle: Geschäftsmodelle, die mit minimalen Kosten auf größere Märkte ausgeweitet werden können – wie Software oder digitale Plattformen – sind ideal für Investoren.
- Attraktive Märkte: Branchen wie Technologie, Biotechnologie, erneuerbare Energien oder Trends wie Nachhaltigkeit und KI bieten spannende Investmentmöglichkeiten durch hohe Wachstumsraten und Innovationskraft.
In welcher Phase wird investiert?
Venture Capital wird in unterschiedlichen Phasen eines Unternehmens eingesetzt, abhängig von der Strategie der VC-Gesellschaft. In der Seed-Phase werden Start-ups unterstützt, die sich noch in der Ideenfindung oder Produktentwicklung befinden. In der Start-up-Phase erhalten Unternehmen Mittel, um ein marktfähiges Produkt einzuführen und erste Kunden zu gewinnen. In der Expansions-Phase wird das Kapital genutzt, um in neue Märkte zu expandieren, das Wachstum zu beschleunigen und den Marktanteil zu erhöhen. Jede Phase birgt spezifische Risiken, aber auch Chancen, was die Auswahl und den Zeitpunkt der Investition besonders wichtig macht.
Typische Aufgaben und Verantwortlichkeiten im Venture Capital
Die Arbeit im Venture Capital ist vielseitig und reicht von der Analyse vielversprechender Start-ups bis hin zur strategischen Unterstützung nach einer Investition. Die Aufgaben lassen sich grob in drei Hauptbereiche unterteilen:
- Start-up-Suche und Bewertung:
Eine der zentralen Aufgaben ist das „Deal Sourcing“, also das Aufspüren potenzieller Investmentmöglichkeiten. Hierbei sind ein gutes Netzwerk und Branchenkenntnisse entscheidend. Nach der Identifikation interessanter Start-ups folgt dann die Analyse. - Investmentmanagement:
Sobald ein Investment zustande kommt, geht es um die Zusammenarbeit mit dem Start-up. Dazu gehören die Überwachung der Unternehmensentwicklung, die Teilnahme an strategischen Entscheidungen und gegebenenfalls die Bereitstellung von zusätzlichen Ressourcen, sei es in Form von Kapital oder Know-how. VC-Manager:innen sitzen oft im Beirat der Start-ups und stehen in engem Austausch mit dem Gründerteam. - Exit-Strategien planen und umsetzen:
Ein wichtiger Aspekt der Arbeit im Venture Capital ist der „Exit“ – also der Verkauf der Unternehmensanteile, um eine Rendite zu erzielen. Dies kann beispielsweise über einen Börsengang (IPO, bzw. Initial Public Offering) oder den Verkauf an andere Unternehmen (Trade Sale) erfolgen. Die Planung und Umsetzung dieser Exit-Strategien ist essentiell, um den finanziellen Erfolg des Investments zu maximieren.
Neben diesen Kernaufgaben kommen weitere Verantwortlichkeiten hinzu, wie der Aufbau und die Pflege von Netzwerken, das Verständnis aktueller Markttrends und die Weiterentwicklung der eigenen Investmentstrategie.
Karrierewege im Venture Capital
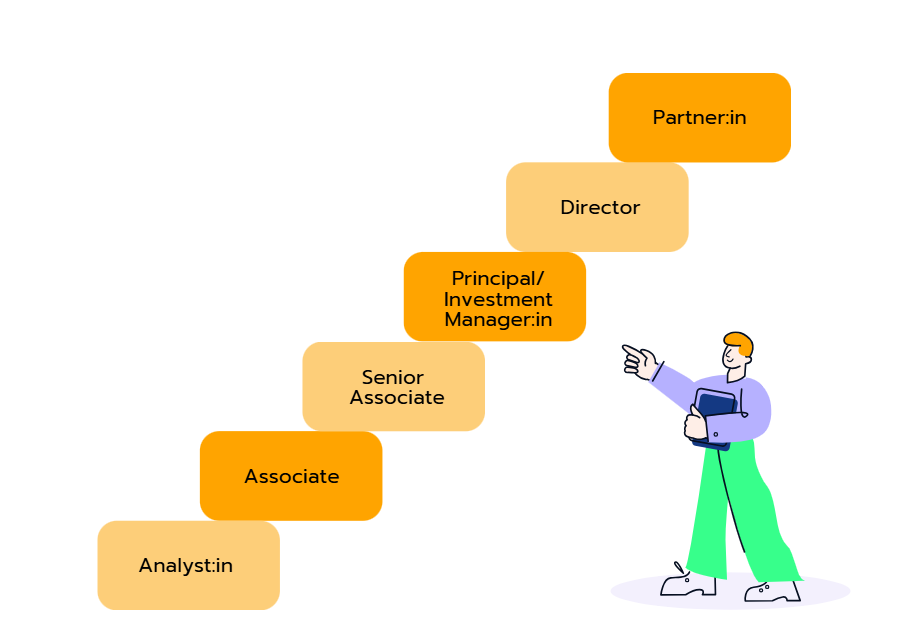
Die Karriere im Venture Capital folgt einem klaren und strukturierten Pfad, der dir vielfältige Entwicklungsmöglichkeiten bietet. In der Regel startest du als Analyst:in, wo du Märkte analysierst, Geschäftsmodelle bewertest und den Investmentprozess, insbesondere bei der Due Diligence, unterstützt. Mit zunehmender Erfahrung kannst du zum Associate und später zum Senior Associate aufsteigen. In diesen Rollen übernimmst du mehr Verantwortung, insbesondere bei Verhandlungen und der Betreuung von Portfoliounternehmen. Als Senior Associate bist du zudem intensiver in strategische Entscheidungen und die Strukturierung von Deals eingebunden.
Der nächste Karriereschritt führt dich zur Position als Principal oder Investment Manager:in. Hier trägst du eigenständig Verantwortung für Investitionen, leitest den gesamten Investmentprozess und setzt wichtige strategische Initiativen um. Anschließend kannst du zum Director aufsteigen, wo du größere Portfolios führst, Netzwerke aufbaust und aktiv zur Weiterentwicklung der Investmentstrategie beiträgst.
Der Höhepunkt der Karriere ist die Rolle als Partner:in. In dieser Position gestaltest du die Investmentstrategie der Firma maßgeblich mit, baust entscheidende Netzwerke aus und konzentrierst dich auf die Akquise von Kapital für neue Fonds. Jede Stufe in dieser Laufbahn bietet dir neue Herausforderungen und Chancen, deine Fähigkeiten weiterzuentwickeln und einen spürbaren Einfluss auf die Zukunft der Branche zu nehmen.
Welches Gehalt kannst du im Venture Capital erwarten?
Das Gehalt im Venture Capital variiert je nach Position, Berufserfahrung und Unternehmensgröße, liegt jedoch oft über dem Durchschnitt in der Finanzbranche.
Analyst:innen können mit einem Jahresgehalt zwischen 50.000 und 80.000 Euro rechnen, abhängig von Standort und Firmengröße. Associates, die mehr Verantwortung tragen, verdienen meist zwischen 80.000 und 120.000 Euro jährlich, oft ergänzt durch Boni.
In höheren Positionen wie Principals oder Investment Manager:innen steigt das Gehalt deutlich und kann inklusive variabler Vergütungen 150.000 bis 300.000 Euro erreichen.
Partner:innen gehören zu den Top-Verdienern und profitieren zusätzlich von sogenannten „Carried Interests“, also Anteilen an den Gewinnen der Fonds, was ihr Einkommen erheblich steigern kann. Venture Capital bietet somit wirklich attraktive finanzielle Perspektiven.
Wichtige Fähigkeiten und Qualifikationen für eine Karriere im Venture Capital
Erfolg im Venture Capital erfordert eine vielseitige Mischung aus fachlichen und persönlichen Fähigkeiten, die aufeinander abgestimmt sein müssen, um in dieser anspruchsvollen Branche zu überzeugen:
- Analytische Fähigkeiten: Die Fähigkeit, große Datenmengen schnell zu verarbeiten und zu interpretieren, ist entscheidend. Dies umfasst unter anderem die Bewertung von Finanzkennzahlen, die Durchführung von Marktanalysen und das Erkennen von Trends, die das Potenzial eines Start-ups beeinflussen können.
- Kenntnisse in Finanzen und Unternehmensbewertung: Ein fundiertes Verständnis von Finanzierungskonzepten, Bewertungsmethoden und Investitionsstrategien ist unerlässlich. Du musst in der Lage sein, Geschäftsmodelle kritisch zu hinterfragen, Risiken zu identifizieren und Chancen objektiv zu bewerten.
- Strategisches Denken: Im Venture Capital geht es nicht nur um die Analyse von Zahlen, sondern auch darum, das „große Ganze“ zu verstehen. Dazu gehört die Fähigkeit, Marktveränderungen vorauszusehen und strategisch zu planen, wie ein Start-up diese nutzen kann, um langfristig erfolgreich zu sein.
- Kommunikationsstärke: Der Erfolg einer Investition hängt oft von der Zusammenarbeit mit Gründerteams ab. Deshalb ist es wichtig, komplexe Sachverhalte klar und verständlich zu vermitteln, Vertrauen aufzubauen und auch in schwierigen Situationen konstruktiv zu kommunizieren.
- Verhandlungsgeschick: Investitionsentscheidungen erfordern häufig intensive Verhandlungen – sei es bei der Bewertung eines Start-ups, der Gestaltung von Vertragsbedingungen oder der Sicherung von Unternehmensanteilen. Ein gutes Verhandlungsgeschick kann hier den Unterschied machen.
Relevante Abschlüsse und Weiterbildungen für eine Karriere im Venture Capital
Ein solider akademischer Hintergrund ist in der Regel eine Voraussetzung für den Einstieg ins Venture Capital. Besonders gefragt sind Abschlüsse in Wirtschaftswissenschaften, Finanzen, Ingenieurwesen oder Informatik. Diese Fachrichtungen bieten die notwendigen Grundlagen, um Märkte zu analysieren, Geschäftsmodelle zu bewerten und innovative Technologien zu verstehen. Absolvent:innen technischer Disziplinen punkten zusätzlich mit ihrem Wissen über spezialisierte Branchen wie Künstliche Intelligenz, Biotechnologie oder Softwareentwicklung – Bereiche, die für Venture Capital besonders attraktiv sind.
Weiterbildungen wie ein MBA können ebenfalls von Vorteil sein, insbesondere für Kandidat:innen, die sich beruflich weiterentwickeln oder von anderen Bereichen, wie Consulting oder Investment Banking, in die Venture-Capital-Branche wechseln möchten. Ein MBA vermittelt nicht nur tiefere Einblicke in Finanzierungs- und Managementstrategien, sondern hilft auch, Netzwerke zu knüpfen, die in der Branche oft entscheidend sind. Zusätzlich gibt es spezialisierte Programme und Zertifikate, die sich direkt auf Venture Capital oder Private Equity konzentrieren und praxisorientierte Kenntnisse vermitteln.
Neben der theoretischen Qualifikation sind praktische Erfahrungen ebenso wichtig. Tätigkeiten als Praktikant:in oder Werkstudent:in in VC-Firmen oder verwandten Bereichen wie Investment Banking oder Start-ups bieten dir wertvolle Einblicke in die Branche. Gleichzeitig kannst du dabei wichtige Kontakte knüpfen, die dir später von Nutzen sein können.
Fazit: Die wichtigsten Key Takeaways
- Venture Capital unterstützt junge, wachstumsstarke Unternehmen dabei, ihre innovativen Ideen umzusetzen und ganze Branchen zu transformieren.
- Von der Start-up-Suche über die Due Diligence bis hin zur Begleitung nach der Investition folgt der Investmentprozess klar definierten Schritten, um Chancen zu maximieren und Risiken zu minimieren.
- Attraktive Start-ups überzeugen durch innovative Ideen, hohes Wachstumspotenzial, skalierbare Geschäftsmodelle und ein starkes Gründerteam. Märkte wie Technologie, Biotechnologie und Nachhaltigkeit stehen besonders im Fokus.
- Der Einstieg erfolgt meist als Analyst:in, mit klaren Aufstiegsmöglichkeiten bis zur Partner-Position. Die Gehälter sind attraktiv und steigen mit wachsender Verantwortung. Spitzenverdiener profitieren zusätzlich von Fonds-Gewinnen („Carried Interests“).
- Neben einem fundierten akademischen Hintergrund – oft in Wirtschaft, Finanzen oder Technik – sind analytische Fähigkeiten, strategisches Denken und Kommunikationsstärke entscheidend. Praktische Erfahrungen und Weiterbildungen wie ein MBA verschaffen dir zusätzliche Vorteile.
Venture Capital ist eine spannende und anspruchsvolle Branche, die nicht nur beruflich herausfordernd ist, sondern auch einen echten Einfluss auf die Zukunft von Innovationen und Technologien bietet. Also, worauf wartest du?
Lerne noch mehr