Investment banking interviews can be rigorous, with a significant focus on technical knowledge. As a candidate, it is crucial to be well-prepared to answer a variety of technical questions that test your understanding of finance, accounting, valuation, and market analysis. This guide aims to provide you with a set of potential questions and ideal answers, along with practical tips to help you succeed in your investment banking interview.


Preparing for Technical Questions in Investment Banking Interviews
25 Common Technical Questions and Ideal Answers in the Investment Banking Interview
1. What are the three main financial statements?
Answer: The three main financial statements are the Income Statement, the Balance Sheet, and the Cash Flow Statement. The Income Statement shows a company's revenues and expenses over a period of time. The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity at a specific point in time. The Cash Flow Statement shows the inflows and outflows of cash within a company during a given period.
2. How do the three financial statements link together?
Answer: The financial statements are interconnected. The net income from the Income Statement flows into the Balance Sheet as retained earnings and into the Cash Flow Statement as the starting point for operating activities. The ending balance of cash on the Cash Flow Statement flows back into the Balance Sheet under the cash account.
3. What is EBITDA and why is it important?
Answer: EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It is a measure of a company's operating performance and is used to compare profitability between companies and industries because it eliminates the effects of financing and accounting decisions.
4. What is a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis?
Answer: A DCF analysis is a valuation method used to estimate the value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows. These cash flows are projected and then discounted back to their present value using the company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
5. How do you calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC)?
Answer: WACC is calculated by taking the proportion of each source of capital (equity, debt, etc.), multiplying each by its respective cost, and then summing the results. The formula is:
WACC = (E/V×Re) + ((D/V×Rd) × (1−Tc))
where E is the market value of equity, V is the total value of equity and debt, Re is the cost of equity, D is the market value of debt, Rd is the cost of debt, and Tc is the corporate tax rate.
6. What is the difference between enterprise value and equity value?
Answer: Enterprise value is the total value of a company, including debt, equity, and cash. It is calculated as Market Capitalization + Debt + Minority Interest + Preferred Shares - Cash and Cash Equivalents. Equity value, on the other hand, represents the value of shareholders' equity, which is Market Capitalization.
7. What are the main valuation methods?
Answer: The main valuation methods are Comparable Company Analysis, Precedent Transactions, and Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis. Comparable Company Analysis involves valuing a company based on the valuation multiples of similar companies. Precedent Transactions analysis involves valuing a company based on the prices paid in similar past transactions. DCF Analysis values a company based on its expected future cash flows.
8. Explain the concept of free cash flow.
Answer: Free cash flow is the cash generated by a company after accounting for capital expenditures needed to maintain or expand the asset base. It is calculated as:
Free Cash Flow = Operating Cash Flow − Capital Expenditures
9. What is accretion/dilution analysis?
Answer: Accretion/dilution analysis is used to assess the impact of an acquisition on the acquirer's Earnings Per Share (EPS). If the combined EPS post-acquisition is higher than the acquirer's standalone EPS, the transaction is accretive. If it is lower, the transaction is dilutive.
10. What is leverage and why is it important?
Answer: Leverage refers to the use of borrowed funds to finance the purchase of assets. It is important because it can amplify returns on investment, but it also increases risk since debt must be repaid regardless of the company's financial performance.
11. What are some common multiples used in valuation?
Answer: Common multiples include Price-to-Earnings (P/E), Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA), Enterprise Value-to-Sales (EV/Sales), and Price-to-Book (P/B).
12. How would you value a private company?
Answer: Valuing a private company can be done using the same methods as for a public company (Comparable Company Analysis, Precedent Transactions, DCF), but adjustments may be needed for lack of marketability and liquidity. Private company valuations often rely more on precedent transactions and DCF due to the lack of market data.
13. What is a merger and acquisition (M&A) synergy?
Answer: Synergies refer to the potential financial benefit achieved through the combining of companies. Synergies can be cost synergies (reducing costs) or revenue synergies (increasing revenue).
14. What is the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)?
Answer: CAPM is a model that describes the relationship between systematic risk and expected return for assets, particularly stocks. The formula is:
Expected Return = Risk − Free Rate + Bet × (Market Return − Risk − Free Rate)
15. Explain the difference between beta and alpha in finance.
Answer: Beta measures the volatility or systematic risk of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole. Alpha measures the performance of a security or portfolio relative to the market, indicating the excess return achieved.
16. What is a leveraged buyout (LBO)?
Answer: An LBO is a transaction where a company is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the purchase cost. The assets of the company being acquired are often used as collateral for the loans.
17. What is working capital and how is it calculated?
Answer: Working capital is a measure of a company's short-term liquidity. It is calculated as:
Working Capital = Current Assets − Current Liabilities
18. What are the different types of debt financing?
Answer: Types of debt financing include term loans, revolving credit facilities, bonds, and commercial paper. Each has different terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules.
19. What is the difference between primary and secondary markets?
Answer: The primary market is where new securities are issued and sold for the first time, such as through an initial public offering (IPO). The secondary market is where existing securities are traded among investors.
20. What is a credit default swap (CDS)?
Answer: A CDS is a financial derivative that allows an investor to swap or offset their credit risk with that of another investor. Essentially, it acts as a form of insurance against the default of a borrower.
21. How do you perform a sensitivity analysis?
Answer: Sensitivity analysis involves changing one or more input variables to see how those changes impact an outcome or model. It helps in understanding the robustness of financial models under different scenarios.
22. What is the purpose of a financial model?
Answer: A financial model is used to forecast a company’s future financial performance based on historical data and assumptions about future growth, costs, and market conditions. It helps in decision-making for investments, acquisitions, and other strategic initiatives.
23. What is a covenant in a loan agreement?
Answer: Covenants are conditions or clauses included in a loan agreement that the borrower must adhere to. They can be affirmative (actions the borrower must take) or negative (actions the borrower must avoid).
24. Explain the difference between a bond’s coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM).
Answer: The coupon rate is the annual interest rate paid by the bond’s issuer based on the bond’s face value. Yield to maturity (YTM) is the total return anticipated if the bond is held until it matures, considering its current market price, coupon payments, and time to maturity.
25. What is the difference between a stock split and a reverse stock split?
Answer: A stock split increases the number of shares outstanding by issuing more shares to existing shareholders, reducing the stock price. A reverse stock split reduces the number of shares outstanding by consolidating shares, increasing the stock price.
Tips to Prepare for the Investment Banking Interview
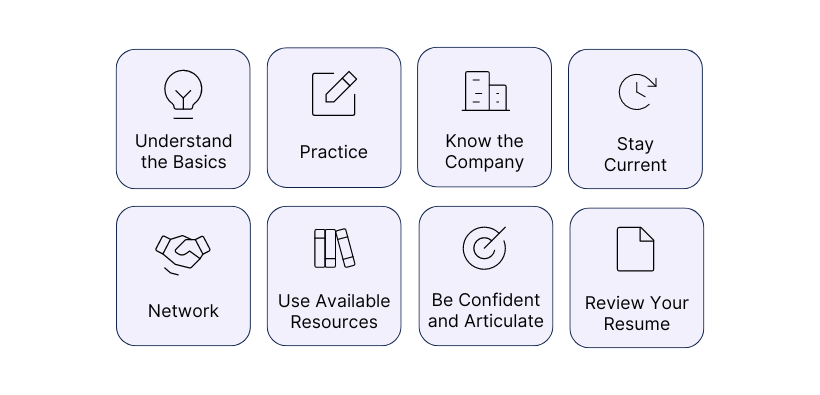
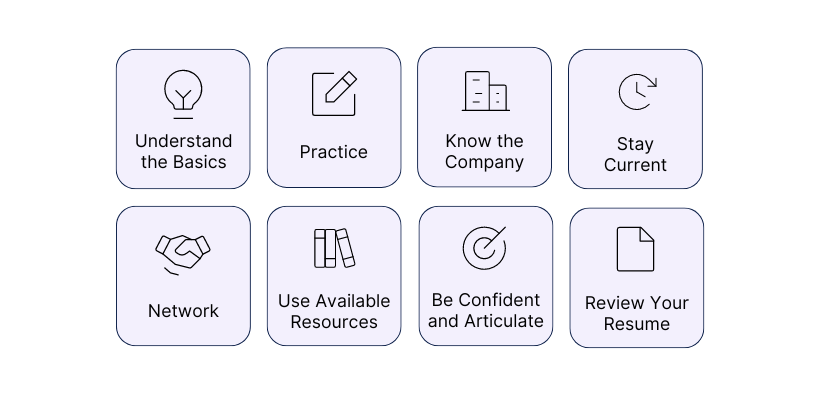
- Understand the Basics: Make sure you have a solid grasp of fundamental finance and accounting concepts. Review textbooks, online resources, and financial news to stay updated.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Practice answering common technical questions out loud. Use mock interviews with friends or mentors to simulate the interview experience.
- Know the Company: Research the specific bank you are interviewing with. Understand their recent deals, market position, and unique aspects of their business.
- Stay Current: Keep up-to-date with the latest market trends, economic news, and developments in the finance industry. This will help you in both technical and fit questions.
- Network: Connect with professionals in the industry through networking events, LinkedIn, or informational interviews. Their insights can be invaluable in understanding what to expect.
- Use Available Resources: Leverage online courses, finance blogs, and study guides specifically geared towards investment banking interviews.
- Be Confident and Articulate: During the interview, be confident in your answers and articulate your thought process clearly. If you don't know an answer, it's better to admit it honestly and demonstrate a willingness to learn.
- Review Your Resume: Be prepared to discuss everything on your resume in detail, including any internships, projects, or relevant coursework.
By following these guidelines and thoroughly preparing, you will definitely increase your chances of performing well in your investment banking interview. Good luck!
Continue to Learn