When you hear the word auditing, it might not sound like the most exciting career at first. But in reality, it’s a fascinating and essential field that shapes businesses, investors, and the entire economy. If you’re thinking about a career as an auditor, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know — from responsibilities and career paths to key requirements and the top companies in the industry. Let’s get started!
Your Career in Auditing — Everything You Need to Know!
What Is Auditing?
Auditing plays a crucial role in companies and financial systems. Essentially, it’s about reviewing a company’s financial statements to ensure they are accurate and complete. This means carefully analyzing annual reports, balance sheets, and other financial documents. The goal is to verify that these records comply with legal standards and provide a clear, honest view of a company’s financial health.
Auditing is crucial for a variety of reasons and impacts many stakeholders. For companies, it ensures their financial reporting is reliable, helping build trust with business partners, banks, and clients. Without this verification, securing loans, attracting investors, or maintaining a strong reputation could become challenging.
For investors, auditing is an essential tool to determine whether a company is as stable and profitable as it claims to be. Without solid, verified data, investment decisions could rely on false assumptions — leading to costly mistakes.
Moreover, auditing provides valuable insights that drive strategic decisions. This includes optimizing internal processes, identifying new market opportunities, or adapting to regulatory changes. Ultimately, it contributes to the stability and growth of the broader economy.
The Main Responsibilities in Auditing
The primary task of auditors is to review annual financial statements and balance sheets. They ensure that a company’s financial reporting complies with legal requirements and provides an accurate picture of its financial position. In practice, this means verifying that revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities are correctly and transparently presented.
However, an auditor’s work goes far beyond this core responsibility. Here’s an overview of other key tasks:
- Consulting on Internal Processes
Auditors don’t just focus on the numbers — they also look at how those numbers are generated. They analyze a company’s internal workflows, such as how invoices are processed, inventory is managed, or payments are monitored. If they identify weaknesses, like inefficient processes or missing controls, they provide recommendations for improvement. The goal is to minimize errors and make operations more efficient and secure. - Tax Audits
Another key area of responsibility is reviewing tax-related matters. Auditors ensure that companies meet their tax obligations. This isn’t just about avoiding mistakes but also identifying and reducing tax risks early on. For example, they verify that all tax-relevant transactions are properly documented and reported. - Special Audits
In cases such as mergers, acquisitions, or major investments, auditors play a critical role. They assess whether the financial data of a company being acquired is accurate. Their expertise is also essential during IPOs, ensuring that all relevant figures are fully and transparently disclosed. - Compliance Audits
In highly regulated industries like finance or pharmaceuticals, compliance with legal requirements is important. Auditors check whether companies are adhering to these regulations and uncover any violations before they escalate into serious issues. - Risk Assessment
Beyond examining financial data, auditors also focus on assessing risks that could impact a company. This includes analyzing factors like market fluctuations, credit risks, or changes in legislation. - IT Systems Audits
Since most financial data is processed digitally, auditors also review the IT systems used for accounting and financial reporting. They ensure that these systems are reliable and free from vulnerabilities that could cause errors or security breaches.
Career Paths in Auditing
If you’re considering a career in auditing, it’s worth taking a closer look at the wide range of opportunities available. Whether you prefer a traditional path with clear promotion steps or want to specialize in a particular area, you have the flexibility to shape your career to match your goals. Below, we’ll explain how a typical career path in auditing is structured and highlight some alternative growth opportunities.
The Hierarchy in Auditing
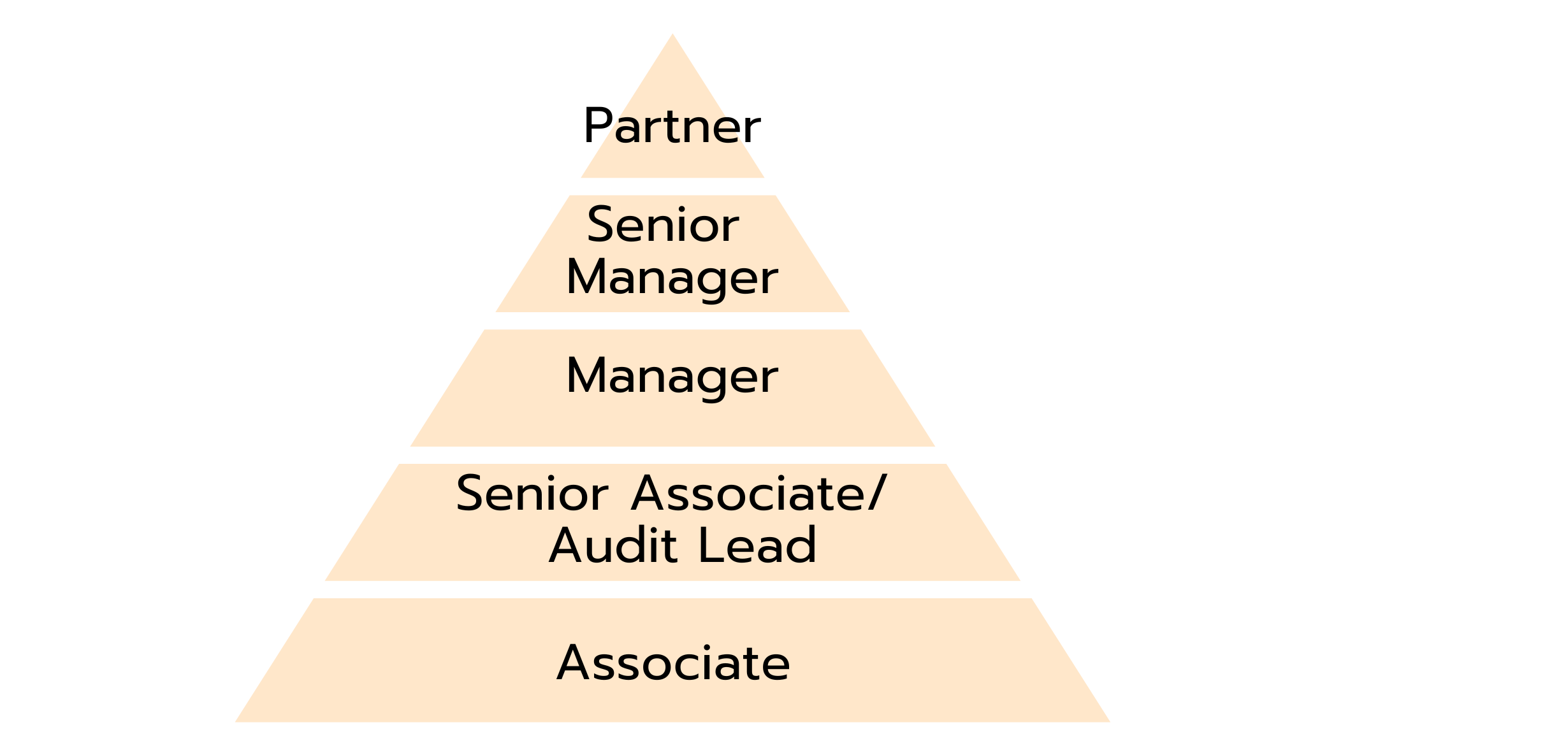
As in many other industries, auditing has a clear hierarchy that provides structure and guidance for your career progression. Most people start their journey as an Associate, often right after graduating. In this role, you’ll support experienced colleagues by assisting with audits of financial statements, preparing reports, and learning the fundamentals of the job.
With growing experience, you can advance to Senior Associate or Audit Lead. Here, you take on more responsibility, coordinate smaller audit projects, and interact directly with clients.
The next step brings you to the position of Manager, where you oversee larger audit projects, lead your team and maintain client relationships. At this stage, the focus shifts to strategic planning and further developing your expertise.
As your skills and experience deepen, you can move into a Senior Manager role. In this position, you manage particularly complex and high-profile mandates, explore new business opportunities and play a key role in the company’s leadership and strategic direction.
At the top of the career ladder is the position of Partner. As a Partner, you are primarily responsible for shaping the firm’s strategic vision, acquiring new clients, and actively contributing to the company’s long-term success.
Fields of Work and Alternative Career Paths in Auditing
As an auditor, you have the opportunity to work in various environments depending on your focus and career path. Here are the most common fields of work:
- Audit Firms
Most auditors work in specialized audit and consulting firms. These include large international companies like the Big Four (Deloitte, EY, KPMG, and PwC), as well as mid-sized firms or smaller local audit offices. In this role, you’ll often work on-site with clients to audit their finances and processes. - Companies
Some auditors transition into internal roles within a company’s finance or controlling department. Here, you’ll typically handle internal audits or ensure compliance with regulations and standards. - Public Sector
There’s also demand for auditors in the public sector, such as in government audit offices responsible for reviewing state finances, or in other regulatory agencies focused on financial oversight. - Self-Employment
Experienced auditors can also start their own business, offering services directly to companies or individuals. This is particularly common in areas like tax consulting or providing independent evaluations and reports. - Consulting and Specialization
Over time, you can specialize in areas beyond traditional auditing, such as IT audits, sustainability reporting (ESG), or M&A transactions. These roles go beyond checking numbers and systems: you’ll advise companies on improving processes or preparing for regulatory changes. This combination of auditing and consulting offers exciting challenges and makes you a sought-after expert in your field.
Required Qualifications and Skills in Auditing
To succeed as an auditor, you’ll need a combination of technical qualifications and personal strengths. To give you a clear overview, we’ve outlined the key requirements below.
A Relevant Degree as a Foundation
A degree is the first step on the path to becoming an auditor. While a degree in economics or business is not strictly required, around 85% of practicing auditors hold one. This is because business-related content — such as accounting, tax law and controlling — provides an ideal foundation for the auditor’s exam.
If you choose this route, programs such as Business Administration, Economic, Business Law, or Finance can be an advantage. It’s highly recommended to focus on areas like auditing, corporate taxation, or accounting during your studies, as these subjects equip you with the knowledge you’ll need for both the exam and your professional career.
Alternatively, degrees in engineering or law can also serve as a strong entry point, especially if you specialize in areas like tax law, auditing, or financial management. What matters most is building a solid foundation in business-relevant topics, as this will serve as the backbone for your future career path.
Gaining Initial Work Experience
After completing your studies, gaining practical experience at an auditing firm is essential, typically starting in the role of an audit associate. With a master’s degree, you usually need three years of work experience, while a bachelor’s degree requires four years. Internships at auditing firms during your studies can also provide valuable early exposure, giving you insights into the day-to-day work and requirements of the profession while easing your transition into the field.
During your professional practice, you’ll learn to audit financial statements, advise clients, and collaborate with teams on complex projects. This hands-on experience is essential for qualifying to take the auditor’s exam.
The Auditor’s Exam
The auditor’s exam is the most significant milestone on your journey. Known as one of the most challenging exams in the business world, it covers topics such as auditing, tax law, business administration, economics, and business law. Thorough preparation is key — both academically and mentally — as the failure rates are notably high. Passing the exam officially qualifies you to work as a certified auditor.
Personal Competencies
In addition to technical knowledge, personal skills are crucial for your success as an auditor. The profession demands a diverse skill set, as you’ll work with complex data, demanding clients, and varying projects on a daily basis. The following skills are particularly important:
- Analytical Thinking
Analyzing numbers and identifying patterns will be part of your daily routine. You need to spot irregularities and develop solutions — a skill that’s very important in complex projects like mergers or valuations. - Communication Skills
As the bridge between teams and clients, you must present findings clearly and effectively. At the same time, sensitivity is essential when addressing delicate topics, such as risks or weaknesses. - Attention to Detail
Your work influences major decisions, so an eye for detail is a must to avoid errors and ensure reliable results. - Flexibility and Resilience
Every day brings new challenges. Managing shifting projects and tight deadlines requires adaptability and the ability to stay focused under pressure. - Tech Know-How
Digital tools and databases are essential to your work. A comfort with technology and the willingness to learn new systems will be a big advantage. - Willingness to Learn
Laws and standards are constantly evolving. Staying committed to continuous learning will keep you up to date and help expand your skills.
The Big Four and Other Auditing Firms
If you’ve already looked into auditing, you’ve likely come across the term "Big Four". These four globally leading firms are renowned not only for their size but also for their influence and prestige. They serve the largest companies worldwide and offer exciting international career opportunities. Starting your career at a Big Four firm can provide you with invaluable experience, excellent networking opportunities, strong career development and competitive salaries.
However, there are also compelling alternatives beyond the Big Four. Firms like BDO, Grant Thornton, or Mazars provide similarly exciting work environments, often with a stronger focus on mid-sized businesses or a more personal workplace culture. These firms may appeal to you if you value flatter hierarchies, specialized roles, or a more regional focus. Depending on your career goals, it’s definitely worth looking beyond the biggest names.
The Big Four at a Glance
To give you an initial impression of the Big Four, here’s a brief overview of each company:
1. PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC)
With over 320,000 employees in 155 countries, PwC is one of the largest networks in auditing and consulting. Founded in 1998 through the merger of Price Waterhouse and Coopers & Lybrand, the firm is headquartered in London. PwC is particularly well known for its work with large multinational corporations and its expertise in sustainability and digital transformation.
👉 Interested in PwC's consulting division? Check out our PwC Interview Guide for valuable insights and tips!
2. Ernst & Young (EY)
EY employs around 365,000 people in over 150 countries and is headquartered in London. The firm invests heavily in technology and innovation, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence and blockchain, to advance auditing and consulting processes. EY is also known for its annual "EY Global Integrity Report," which is recognized globally as a benchmark for transparency and ethical business practices.
3. KPMG

KPMG operates in 145 countries and employs over 265,000 people worldwide. Headquartered in Amstelveen, Netherlands, the firm is known for its specialization in highly regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and energy. KPMG increasingly focuses on automated audit processes and offers comprehensive services in cybersecurity.
👉 Prepare thoroughly for your KPMG case interview with our KPMG Interview Guide.
5. Deloitte
![]()
Deloitte is the largest member of the Big Four, with over 415,000 employees in 150 countries. Founded in 1845 and headquartered in London, Deloitte is also the oldest of the Big Four. The firm leads the way in artificial intelligence and data analytics, investing heavily in integrating technology into its auditing and consulting services. Deloitte also enjoys an excellent reputation for advising start-ups and technology companies.
👉 Curious about a career as a consultant at Deloitte? Explore our Deloitte Case Interview Guide for practical tips and expert insights!
Other Prominent Auditing Firms
Here is an overview of some alternative audit firms that might also be very interesting for you:
1. BDO
BDO operates in over 160 countries and employs around 97,000 people worldwide. The firm provides services in auditing, tax consulting, and advisory, with a strong focus on supporting mid-sized companies.
2. Grant Thornton![]()
Grant Thornton operates internationally and specializes not only in auditing but also in consulting services. In Germany, the firm is well-known for its expertise in serving family-owned businesses and mid-sized companies.
3. Forvis Mazars
Forvis Mazars operates in over 90 countries and offers a wide range of services beyond auditing, including tax consulting and financial advisory. The firm places a strong emphasis on fostering an inclusive corporate culture and supports its employees' development through diverse training programs.
4. Baker Tilly
Baker Tilly operates in over 140 countries, offering services in auditing, tax consulting, and business advisory. The firm focuses on innovative solutions and provides employees with opportunities to work in international teams.
How to Prepare for Auditing Interviews
If you want to start your career as an auditor, you’ll face challenging recruitment processes, especially at top firms like the Big Four. But don’t worry — with the right preparation, you’ll be ready to shine!
- Understand the Industry
Auditing is about more than just crunching numbers. It’s about understanding businesses, reviewing financial statements and ensuring compliance with legal regulations. Stay informed about current trends like digitalization, sustainability (ESG) and regulatory changes — it will make you stand out during interviews. - Train Your Technical Knowledge
A solid foundation is key: Get familiar with standards like International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (U.S. GAAP), as well as basic tax laws. Practice case studies, like analyzing financial statements — these tasks often come up in case interviews. - Highlight Your Soft Skills
Your personal skills are just as important as your technical knowledge. During group exercises or interviews, focus on clear communication, teamwork, and time management. Auditing is all about teamwork, often under tight deadlines. Practice Common Questions
Prepare for questions like “Why do you want to become an auditor?” or “Why do you want to work for us?”. Show your motivation and understanding of the firm. Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to structure your answers clearly and effectively.👉 Use our stress question tool to prepare for challenging interview scenarios!
- Network Strategically
Connect with employees or trainees from your target firm — whether at career fairs or on LinkedIn. Some of the best tips come from people who’ve already walked the path, so don’t underestimate the power of networking.
Key Takeaways
Auditing is about far more than reviewing numbers — it’s a vital part of the economy, fostering trust, transparency, and stability for businesses and investors. It also provides insights that extend well beyond finance.
If you’re pursuing a career in auditing, you’ll have to manage diverse tasks — from auditing financial statements to consulting in areas like IT, ESG, or M&A. Career paths are clearly structured yet offer room for specialization and personal growth. With the right education, strong technical knowledge and personal strengths like analytical thinking and communication skills, you can be very successful in this dynamic field.
Whether at the Big Four or other international firms, a career in auditing offers exciting opportunities to grow professionally and work at the intersection of numbers, strategy, and innovation.
Continue to Learn