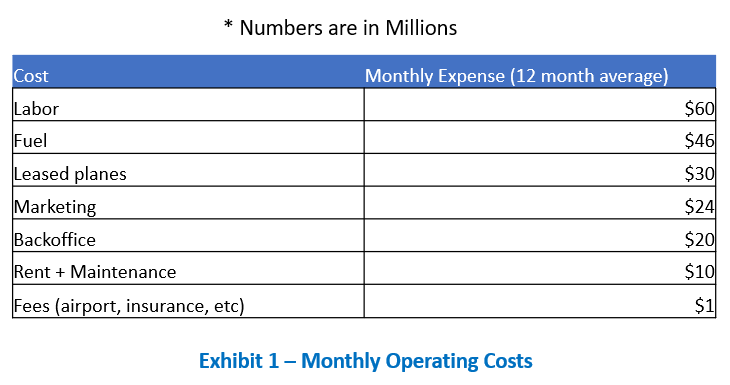
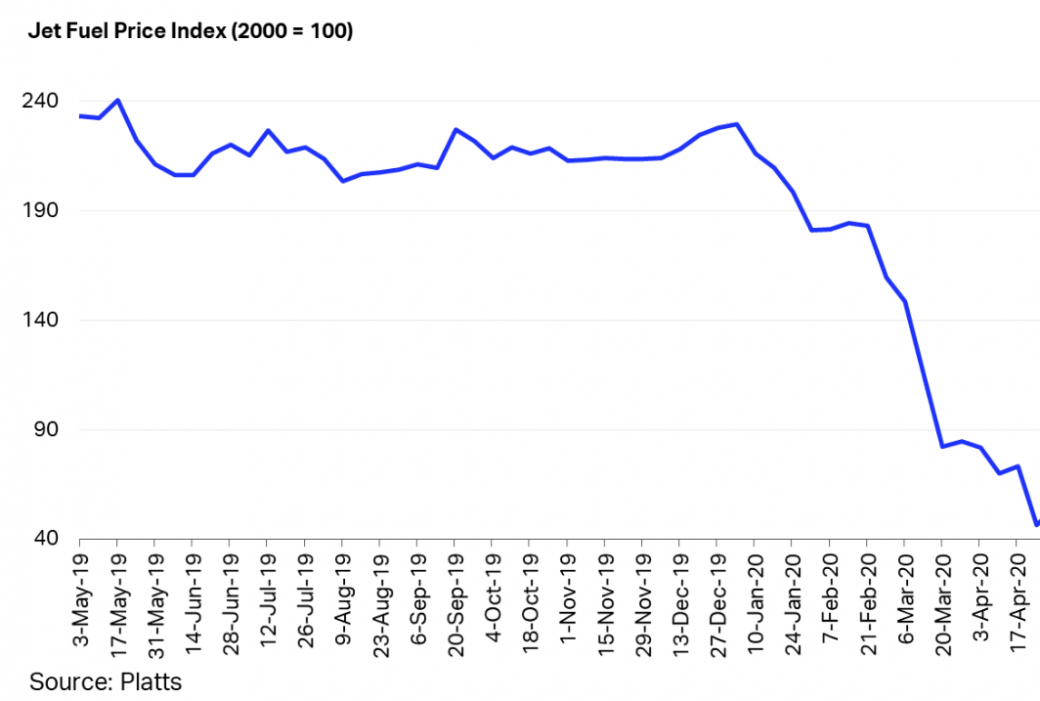
Sky China, a government-backed Chinese airline, has recently seen profits plummet due to COVID-19. Profits are down 80% in the months of February and March, but are showing early signs of a rebound in April.
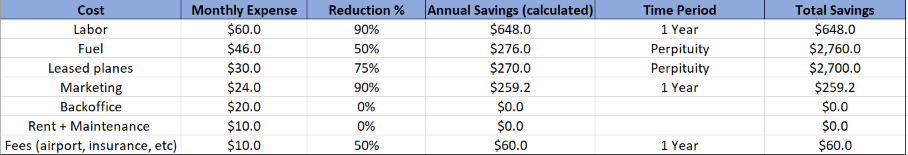
They've brought you in to first investigate what can be done immediatedly to prevent hemorrhaging cash and surive in the short-term. They are also looking to see how the current situation can be viewed as an opportunity, and what can be done to prepare for the future.


MBB - Sky China
i